Prerequisites
The sample relies on the availability of a SQL Server named . and the existence of a database named Samples..
Code walk-through
This sample shows a simple client/server scenario.
Clientsends aStartOrdermessage toServer.Serverstarts anOrderSaga.OrderSagarequests a timeout withCompleteOrderdata.- When the
CompleteOrdertimeout fires, theOrderSagapublishes anOrderCompletedevent. Serverthen publishes a message that the client has subscribed to.Clienthandles theOrderCompletedevent.
NHibernate config
NHibernate is configured with the right driver, dialect, and connection string. Then, since NHibernate needs a way to map the class to the database table, the configuration code does this using the ModelMapper API. Finally, the configuration is used to run the endpoint.
var endpointConfiguration = new EndpointConfiguration("Samples.NHibernate.Server");
var persistence = endpointConfiguration.UsePersistence<NHibernatePersistence>();
// for SqlExpress use Data Source=.\SqlExpress;Initial Catalog=Samples.NHibernate;Integrated Security=True;Max Pool Size=100;Encrypt=false
var connectionString = @"Server=localhost,1433;Initial Catalog=Samples.NHibernate;User Id=SA;Password=yourStrong(!)Password;Max Pool Size=100;Encrypt=false";
var hibernateConfig = new Configuration();
hibernateConfig.DataBaseIntegration(x =>
{
x.ConnectionString = connectionString;
x.Dialect<MsSql2012Dialect>();
x.Driver<MicrosoftDataSqlClientDriver>();
});
AddMappings(hibernateConfig);
persistence.UseConfiguration(hibernateConfig);
Order saga data
Note that to use NHibernate's lazy-loading feature, all properties on the saga data class must be virtual.
public class OrderSagaData :
ContainSagaData
{
public virtual Guid OrderId { get; set; }
public virtual string OrderDescription { get; set; }
}
Order saga
public class OrderSaga :
Saga<OrderSagaData>,
IAmStartedByMessages<StartOrder>,
IHandleTimeouts<CompleteOrder>
{
static ILog log = LogManager.GetLogger<OrderSaga>();
protected override void ConfigureHowToFindSaga(SagaPropertyMapper<OrderSagaData> mapper)
{
mapper.ConfigureMapping<StartOrder>(message => message.OrderId)
.ToSaga(sagaData => sagaData.OrderId);
}
public Task Handle(StartOrder message, IMessageHandlerContext context)
{
Data.OrderId = message.OrderId;
var orderDescription = $"The saga for order {message.OrderId}";
Data.OrderDescription = orderDescription;
log.Info($"Received StartOrder message {Data.OrderId}. Starting Saga");
var shipOrder = new ShipOrder
{
OrderId = message.OrderId
};
log.Info("Order will complete in 5 seconds");
var timeoutData = new CompleteOrder
{
OrderDescription = orderDescription
};
return Task.WhenAll(
context.SendLocal(shipOrder),
RequestTimeout(context, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5), timeoutData)
);
}
public Task Timeout(CompleteOrder state, IMessageHandlerContext context)
{
log.Info($"Saga with OrderId {Data.OrderId} completed");
var orderCompleted = new OrderCompleted
{
OrderId = Data.OrderId
};
MarkAsComplete();
return context.Publish(orderCompleted);
}
}
Handler using ISession
The handler uses the ISession instance to store business data.
public class ShipOrderHandler :
IHandleMessages<ShipOrder>
{
public Task Handle(ShipOrder message, IMessageHandlerContext context)
{
var session = context.SynchronizedStorageSession.Session();
var orderShipped = new OrderShipped
{
Id = message.OrderId,
ShippingDate = DateTime.UtcNow,
};
session.Save(orderShipped);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
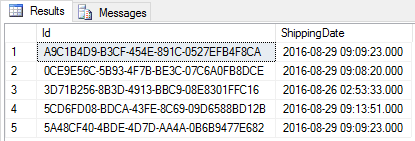
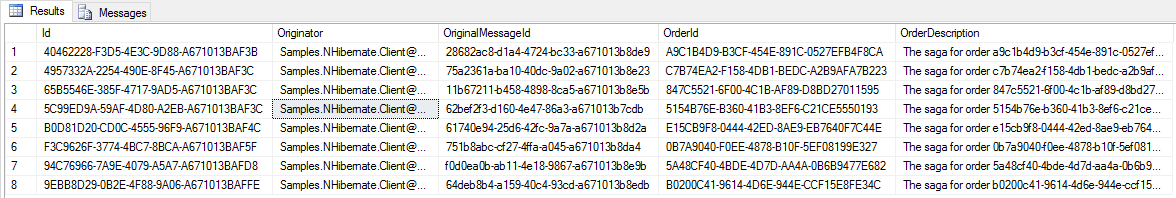
The database
Data in the database is stored in three different tables.
The saga data
IContainSagaData.maps to the OrderSagaData primary key and unique identifier columnId Id.IContainSagaData.andOriginator IContainSagaData.map to columns of the same name with typeOriginalMessageId varchar(255).- Custom properties on SagaData, in this case
OrderDescriptionandOrderId, are also mapped to columns with the same name and the respecting types.
The handler stored data