Every component in the Particular Service Platform (not including NServiceBus), including ServiceControl, must be downloaded and installed.
Install methods
ServiceControl can be installed in multiple ways. This article describes using the visual ServiceControl Management application. Scripted installs and upgrades can be done via the ServiceControl Management PowerShell module. Advanced installation guidance to support high-load and high-availability is available on active/active remote setups and active/passive clustering.
There is also a community-managed puppet module.
Prerequisites
The ServiceControl installation has the following prerequisites:
Planning
In production environments, make sure to review the environment considerations when setting up a machine with ServiceControl.
The ServiceControl Management Utility provides a simple way to set up one or more ServiceControl instances (error, audit, and monitoring). For production systems, it is recommended to limit the number of instances per machine to one of each type. The ability to add multiple instances of the same type on a single machine is primarily intended to assist development and test environments.
See ServiceControl Capacity Planning and Hardware Considerations for more guidance.
Installing ServiceControl instances
There are three types of ServiceControl instances that can be installed using the ServiceControl Management utility. As the error and audit instance usually go side-by-side, they are installed and configured at the same time.
- Open the ServiceControl Management Utility.
- Click the
Newbutton at the top-right and a popup window appears. - Select either
Add ServiceControl and Audit instancesorAdd monitoring instance. - Provide a name and transport.
- The default name is
Particular.. The name is used to derive names for the error and audit instances. The name of each instance can be adjusted from its default if required.ServiceControl - The transport should match the endpoint's transport. If a transport is not available, a transport adapter can be used.
- The default name is
- For additional instance settings, open the
ServiceControlandServiceControl Auditsections.- The name of the instance can be modified; the defaults for error and audit are
Particular.andServiceControl Particular..ServiceControl. Audit - The name of the error instance is especially important to enable plugins to send information to ServiceControl.
- If multiple instances for different systems are installed on the same server, a name like
Particular.is a common option.SystemName
- Select the appropriate user account. Note that ServiceControl instances will run as Windows Services in the background.
- Be aware of the port numbers as these are used by ServicePulse and ServiceInsight to connect to ServiceControl.
- Configure the retention period for each instance.
- Configure the name of the queue that messages should arrive in. This queue is important to endpoints that send error and audit messages to these ServiceControl instances, as well as plugins.
- If needed, configure forwarding queues.
- Full-text search can be turned off for performance reasons if it's not needed.
- The name of the instance can be modified; the defaults for error and audit are
A monitoring instance differs from error and audit instances in its configuration:
- There is no configuration for storage as it only stores data in memory.
- There is no forwarding queue as the messages are specific to ServiceControl monitoring.
- The queue to forward messages that can't be processed to is different, as described in monitoring setup.
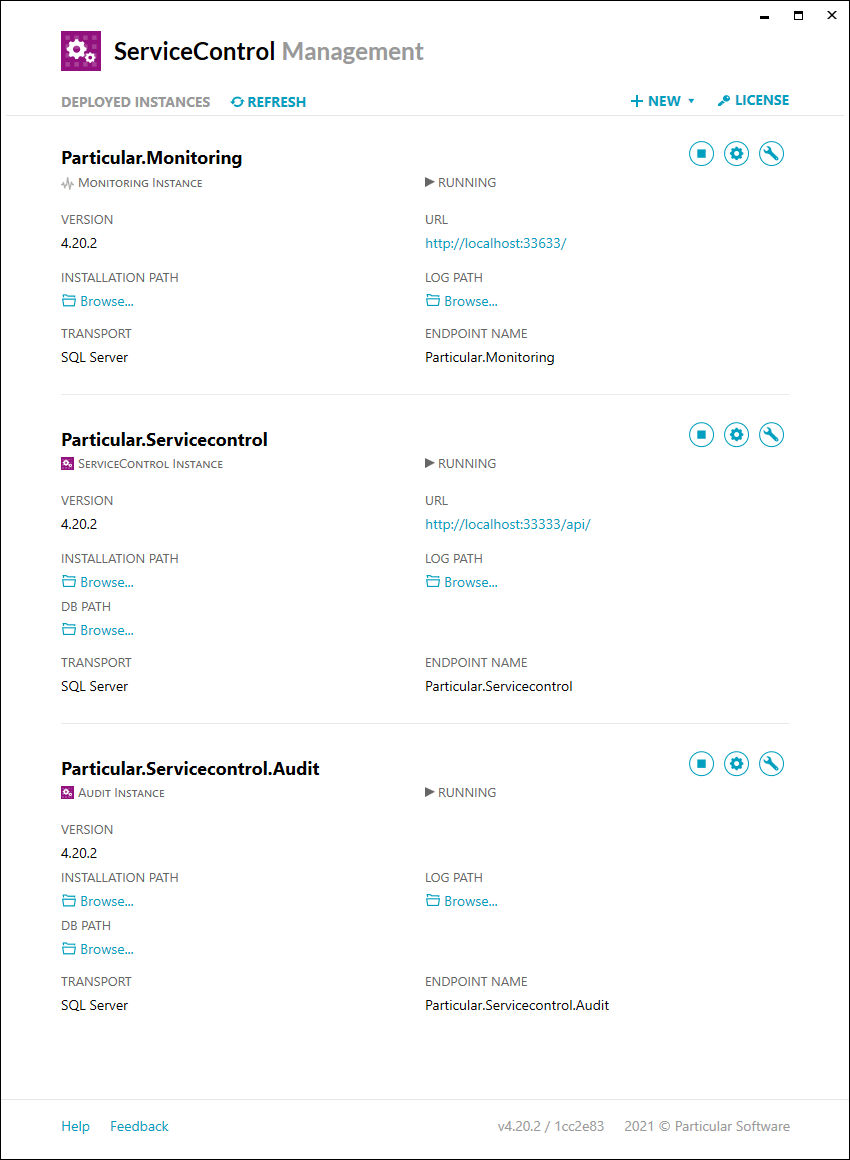
As an example, after configuring an error, audit and monitoring instance for the SQL Server transport, the ServiceControl Management Utility will look similar to this:
Upgrading ServiceControl instances
ServicePulse will show a notification when a new version of ServiceControl is available. New versions can then be downloaded and installed.
The ServiceControl Management Utility displays the instances of the ServiceControl service installed on the current machine. If a ServiceControl instance is running on an outdated version, an upgrade link will be shown next to the version label.
To upgrade the service, click the upgrade link next to the service name.
Clicking the upgrade link will:
- Prompt for additional required information, i.e. new mandatory settings introduced in the newer version
- Stop the service
- Remove the old binaries for ServiceControl and the configured transport
- Run the new binaries to create required queues
- Start the service
Upgrading multiple major versions
A ServiceControl installation should be upgraded one major version at a time. Check the currently installed version of ServiceControl to look up the upgrade path in the table below. For each entry in the upgrade path, install the listed version and upgrade all ServiceControl instances to that version. Once all instances are upgraded and running, install the listed version in the next row until all instances are upgraded to the latest version.
| Current Version | Upgrade Path |
|---|---|
| 1.x.y | Install 1.48.0, and update all instances |
| 2.x.y | Install 2.1.5, and update all instances |
| 3.x.y | Install 3.8.4, and update all instances |
| 4.x.y | Install 4.33.0, and update all instances |
| 5.x.y | Download the latest release, and update all instances |
All versions are available at https://github.com/Particular/ServiceControl/releases
Upgrades might take a while to run. Account for the unavailability of ServiceControl and plan the upgrade during maintenance windows if necessary.
ServiceControl plugins
Endpoint plugins like heartbeats and custom checks require sending information to ServiceControl. The name of the queue is the same name as the error instance.
See Install Heartbeats Plugin and Install Custom Checks Plugin for more information.
Migrating to a new host
To migrate an instance of ServiceControl to another host:
- Ensure the same Windows version is used on the new machine as storage is not compatible between Windows versions
- Stop and disable the current instance of ServiceControl in the Windows Service Manager
- Install and configure a new instance of ServiceControl using the same name on the new server
- Ensure the name is identical
- Stop the newly installed instance of ServiceControl
- Copy the data from the previous instance to the new instance server (moving the data is not recommended)
- Start the new service
- Remove the old instance of ServiceControl
If the database of the instance being migrated is very large, or no downtime can be tolerated, or the destination uses a different Windows version, or the instance uses a different name, then consider scaling ServiceControl out via remote instances.
Things to remember:
- Ensure the instance being migrated is on the latest version.
- Optionally, use the same installer as the current version. Database schemas are not guaranteed to be compatible between versions.
- Optionally, script ServiceControl installations via powershell instead of running installers manually
ServiceControl configuration settings are accessible via the Service Control Management Utility or by navigating to the configuration files on the file system stored in ServiceControl., ServiceControl., and ServiceControl..
If ServiceControl was previously installed via the ServiceControl Management Utility then all instances are installed on a single machine by default. If the system has considerable load or has a large retention period, consider installing a single instance type on a server to scale out. This can be done via Powershell.
Take care when planning to move ServiceControl from one server to another. Moving databases between servers can be challenging. The embedded RavenDB does not support moving from a new version of Windows back to older versions of Windows. See Getting error while restoring backup file in raven DB for more details.
Removing ServiceControl
To perform a clean uninstall of ServiceControl from a machine:
- Remove each ServiceControl instance using the ServiceControl Management Utility (or PowerShell)
- Uninstall the ServiceControl Management Utility using Add or Remove programs
Remove ServiceControl instances
To remove a ServiceControl instance, click the Advanced Options button and select Remove. If applicable, select the option to remove the database and logs directories. This will stop the running instance (if it is running) and remove all files related to the instance from the local file system.
Remaining artifacts
Even after a ServiceControl instance has been removed, there are artifacts left behind. Each ServiceControl instance leaves queues in the configured transport. The queue names will depend on the configuration of the ServiceControl instance.
- instance name - control messages for the ServiceControl instance
- instance name.errors - control messages that the ServiceControl instance was not able to process
- instance name.staging - temporary failed messages while they are being retried
- audit queue name - messages that have been processed by endpoints and then forwarded to the audit queue. These messages have not yet been ingested by the ServiceControl instance.
- error queue name - messages that failed processing in endpoints and have passed immediate and delayed retries. These messages have not yet been ingested by the ServiceControl instance.
- audit log queue name if audit log forwarding was configured - messages that have been ingested from the audit queue, processed by this ServiceControl instance, and then forwarded to the audit log queue.
- error log queue name if error log forwarding was configured - messages that have been ingested from the error queue, processed by this ServiceControl instance, and then forwarded to the error log queue.
If the option to delete the database/log folders was not selected when removing the instance, then these folders and their contents are left on disk.
If the instance was configured to run under a service account then that account may have been granted Logon as a Service privileges. This is not reversed when the instance is removed.